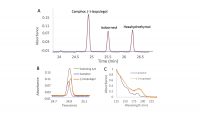
There really is no question that Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs) work, but just how well do they work?
For the last 50+ years, indoor cannabis cultivators have used High Pressure Sodium (HPS) lights to illuminate their flowering crops. This technology was developed for, and is still used, as street lighting and there really hasn’t been a fundamental change to the output in the last half century.LED technology showed great promise to solve some of the primary drawbacks to the use of HPS technology for indoor cannabis cultivation.
We are often asked why this technology was used to grow cannabis, and the answers are simple: 1) due to strict legislation and even stricter penalties for growing cannabis, growers wished to move their crops indoors, and, 2) there really hasn’t been another technology that would allow us to cheaply place 400, 600, or even 1000W of light on a crop. In addition, HPS technology is rich in certain frequencies of red light, which is so important to flowering crops. Unfortunately, HPS lamps have their drawbacks, such as high heat output and lack of other “colors,” along the lighting spectrum. In fact, up to 95% of light produced by an HPS lamp is emitted in the infrared range, which we perceive as heat.
Enter the Light Emitting Diode. LED technology showed great promise to solve some of the primary drawbacks to the use of HPS technology for indoor cannabis cultivation. The ability to manipulate spectrum, precision delivery of light, elimination of dangerous heat, and lack of substantive toxic chemical makeup are a few reasons to deploy LEDs. However, as with any new technology, there were some significant hurdles to overcome.
Early experimentation using Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs) to grow cannabis, suffice to say, did not go well. Poor performance, misleading advertising and equipment failures plagued the first mass-produced LED grow lights. The aspect of poor performance can be blamed on several factors, but the most prominent are very low efficacy, in terms of light produced per Watt consumed, and incorrect application of spectrum (color) for horticultural purposes. Causes of “misleading advertising” was a mixed bag of dubious sales pitches and lack of understanding the technology and of horticultural lighting requirements. Additionally, there certainly were some quality control issues with LEDs and electronics equipment in general, especially from offshore manufacturers in China and Korea.

That legacy of poor performance still has a partial hold on the current indoor cannabis cultivation industry. Many of the current “Master Growers” have tried LEDs at some point and for the various reasons mentioned above, reverted to HPS lighting. Some of this reluctance to embrace LEDs comes from unfamiliarity with application of the technology to grow better cannabis, while some can be attributed to stubbornness to deviate from a decades-long, tried-and-true application of HPS lighting.
Certainly, growing with LEDs require some changes in methodology. For instance, when using true “full spectrum” grow lights, more nutrients are consumed. This is caused by stimulation of more photoreceptors in plants. To further explain, photoreceptors are the trigger mechanisms in plants that start the process of photosynthesis, and each photoreceptor is color/frequency-dependent. True full spectrum LED systems fulfill spectrum shortages experienced with HPS technology. Anyone that grows with LEDs will at some time experience “cotton top,” or bleaching at the upper regions of their plants. Increased nutrient delivery solves this issue.
As we continue to uncover the vast medical potential of cannabis, precise phytochemical composition and consistent quality will become all-important.While the industry is still saturated with confusing rhetoric and some poorly performing equipment, LEDs are gaining momentum in the cannabis market. LED efficacies have increased to levels far greater than any other lighting technology. Broad spectrum white and narrow-frequency LEDs in all visible (and some invisible to the human eye) colors are being produced with great precision and consistency. Quality control in manufacturing is at an all-time high and longevity of LEDs has been proven by the passage of time since their introduction as illumination sources.
As the world embraces LED horticultural lighting, probably the most encouraging news is that current and upcoming generations of cannabis growers are more receptive to new ideas and are much more tech-savvy than their predecessors. Better understanding of cannabis-related photobiology is helping LED grow light manufacturers produce lighting that increases crop yields and perhaps more importantly, cannabis quality. As we continue to uncover the vast medical potential of cannabis, precise phytochemical composition and consistent quality will become all-important.
Obviously, the indoor cannabis industry is expanding rapidly and this expansion raises deep environmental concerns. More power is being used for indoor lighting, and for the cooling required by this lighting. Power systems are being taxed beyond forecasts and in some cases, beyond the capabilities of the infrastructure and power companies’ ability to produce and deliver electricity. Some states have proposed cannabis-related legislature to limit power consumed per square foot, and some are specifically requiring that LEDs be used to grow cannabis. While some business leaders and cultivation operators may groan at the acquisition cost and change in operating procedures when deploying LEDs, common sense states that it is imperative we produce cannabis applying the most environmentally friendly practices available.